
|
Formula |
CAS |
|
C10H12O |
104-46-1 |
CAS: Chemical Abstract Service Registry Number
Background
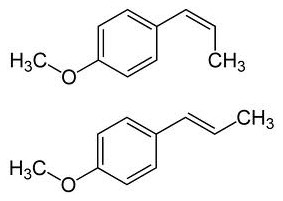
Anethole is the chief constituent of anise, star anise and fennel oils. It is used primarily as a flavoring agent. Anethole (also para-methoxyphenylpropene, p-propenylanisole, and isoestragole) is a phenylpropene, a type of aromatic compound that occurs widely in nature, in essential oils. It contributes a large component of the distinctive flavors of anise and fennel (both in the botanical family Apiaceae), anise myrtle (Myrtaceae), liquorice (Fabaceae), and star anise (Illiciaceae). Closely related to anethole is its double-bond isomer estragole, abundant in tarragon (Asteraceae) and basil (Lamiaceae), that has a flavor reminiscent of anise. Anethole has numerous commercial uses in multiple industries, and high potential for additional uses.
It has two cis-trans isomers, involving the double bond outside the ring. The more abundant isomer, and the one preferred for use, is the trans or E isomer: trans-anethole (CAS nr 4180-23-8), t-anethole, (E)-anethole, trans-para-methoxyphenylpropene. Its full chemical name is trans-1-methoxy-4-(prop-1-enyl)benzene.
Anethole is a flavoring substance of commercial value. In addition, it is distinctly sweet, measuring 13 times sweeter than sugar. It is perceived as being pleasant to the taste even at higher concentrations. Anethole is used in alcoholic drinks, seasoning and confectionery applications, oral hygiene products, and in small quantities in natural berry flavors. Anethole is also present in absinthe, a liquor with a reputation for psychoactive effects; these effects however are attributed to ethanol. Pharmaceutical drugs derived from or related to anethole include anisyldithiolthione, anethole dithione (ADT), and anethole trithione (ATT).
Synonyms
1-Methoxy-4-(1-propenyl)benzene
Anethole
Anise camphor
Monasirup
p-Propenylanisole
Uses
Dentifrices
Microscopy (imbedding agent)
Perfumes
Pharmaceuticals as a flavor
Photography
Soap
Toothpaste
Cross-Reactions
Unusual Reactions
References
|
1. |
Rudzki E, Grzywa Z. Sensitizing and irritating properties of star anise oil. Contact Dermatitis 1976;2(6):305-308. |
|
2. |
Andersen KE. Contact allergy to toothpaste flavors. Contact Dermatitis 1978;4(4):195-198. |
|
3. |
Barratt MD, Basketter DA, Possible origin of the skin sensitization potential of isoeugenol and related compounds. (I). Preliminary studies of potential reaction mechanisms. Contact Dermatitis 1992;27(2):98-104. |
![]() 07-05-2011
(JRM) - www.huidziekten.nl
07-05-2011
(JRM) - www.huidziekten.nl